Upregulation of a Target Cell Can Occur in Response to
Prolonged decrease in the level of a hormone. None of the above.
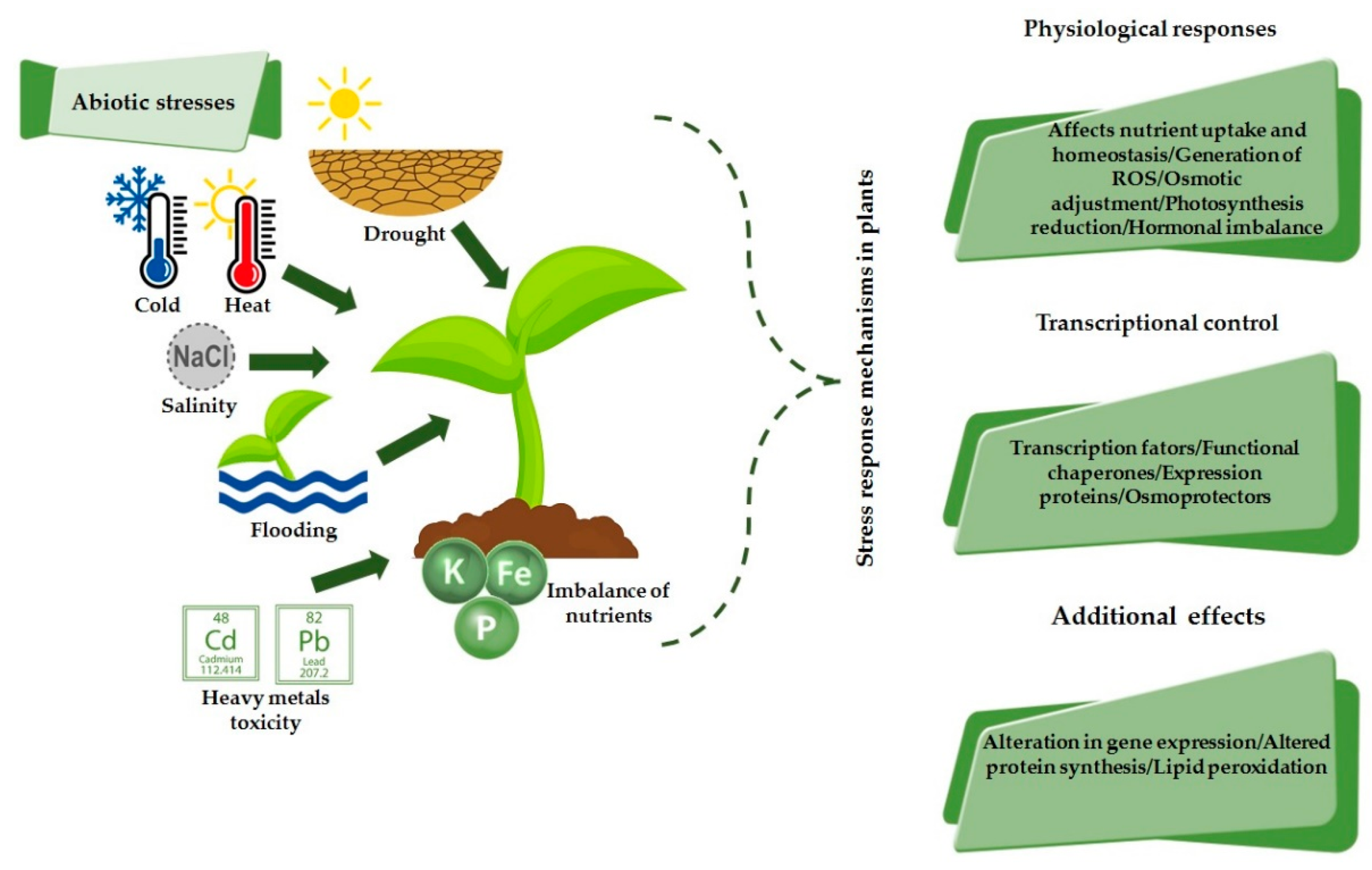
Stresses Free Full Text Physiological Responses To Drought Salinity And Heat Stress In Plants A Review Html
Upregulation of a target cell can occur in response to A prolonged increase in the level of a hormone.
. The opposite of upregulation is downregulation where cells become less. Prolonged decrease in the level of a hormone. Prolonged decrease in the level of a hormone.
Prolonged increase in the level of a hormone. Downregulation is the process by which a cell decreases the quantity of a cellular component such as RNA or protein in response to an external variable. Signals from antagonistic hormone products.
An up regulated cells an increase in. 1- Prolactin PRL 2- Growth hormone 3- TSH 4- ACTH 5-FSH and LH 1- xMammary glands in females and interstitial cells in males correct 2-Almost every cell in the body correct. C prolonged decrease in the level of a hormone.
Prolonged decrease in the level of a hormone. Signals from antagonistic hormone products. Up-regulation of a target cell can occur in response to.
C signals from antagonistic hormone products. Down-regulation of a target cell can occur in response to. An upregulated cell has an increase in A.
A hormone is a _____ and the target cell is _____. Upregulation of a target cell can occur in response to A. Prolonged increase in the level of a hormone.
B prolonged increase in the level of a hormone. Up-regulation of a target cell can occur in response to. Prolonged decrease in the level of a hormone.
Down-regulation of a target cell can occur in response to. 66 Up-regulation of a target cell can occur in response to a prolonged decrease in the level of a hormone. Upregulation Upregulation refers to an increase in the number of receptors due to prolonged deprivation of receptors of interacting with their physiological neurotransmitter eg.
The number of molecules the cell secretes. Up-regulation of a target cell can occur in response to A. 3Upregulation of a target cell can occur in response to Group of answer choices prolonged decrease in the level of a hormone.
Prolonged decrease in hormone levels. Signals from the posterior pituitary. Directly causing protein synthesis.
An increase of a cellular component is called upregulation. None of the answers shown here. Nerve fibers in the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland secrete.
Causing the cell to divide. The concentration of ligands that bind to the receptors. The amount of DNA in the nucleus.
Upregulation is a process that makes cells more responsive to stimuli like hormones by increasing the number of receptors on the surface of the cell. Signals from antagonistic hormone products. A cell that synthesizes hormones.
D signals from the posterior pituitary. An example of downregulation is the cellular decrease in the number of receptors to a molecule such as a hormone or. Prolonged increase in hormone levels.
In the biological context of organisms production of gene products downregulation is the process by which a cell decreases the quantity of a cellular component such as RNA or protein in response to an external stimulus. Signals from antagonistic hormone products. Prolonged decrease in the level of a hormone.
E None of these choices is correct. The complementary process that involves increases of such components is called upregulation. The number of receptors available for binding.
Signals from the posterior pituitary. Prolonged decrease in the level of a hormone. The number of receptors available for binding.
An upregulated cell has an increase in A. A protein that stimulates other cells. The number of receptors available for binding.
The number of receptors available for binding. The concentration of ligands that bind to the receptors. An up-regulated cell has an increase in.
The number of receptors available for binding. By expressing more receptors there is a greater probability that a hormone will bump into and stimulate its receptor. Down-regulation of a target cell can occur in response to A prolonged decrease in the level of a hormone.
Prolonged increase in the level of a hormone. Up-regulation of target cells can occur in response to. Up-regulation of a target cell can occur in response to prolonged decrease in the level of a hormone.
Another name for antidiuretic hormone is. Match the hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary with its target. B signals from antagonistic hormone products.
Prolonged increased in the level of a hormone. By denervation of chronic use of a receptor antagonist. Up-regulation of a target cell can occur in response to.
An example of downregulation is the cellular decrease in. Signals from the posterior pituitary. Up-regulation of a target cell can occur in response to A.
An up-regulation of receptors means that a cell has an increase in. Prolonged decreased in the level of a hormone. Upregulation of a target cell can occur in response to A.
The amount of DNA in the nucleus. The source of hormone secretions B regulatory molecule that controls secretions of other cells. D signals from the posterior pituitary.
The number of molecules the cell secretes. It occurs in response to environmental cues that can vary from changes in hormone levels associated with pregnancy to exposure to toxins.
18 2 How Hormones Work Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
18 2 How Hormones Work Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

Immune Responses To Viral Gene Therapy Vectors Molecular Therapy
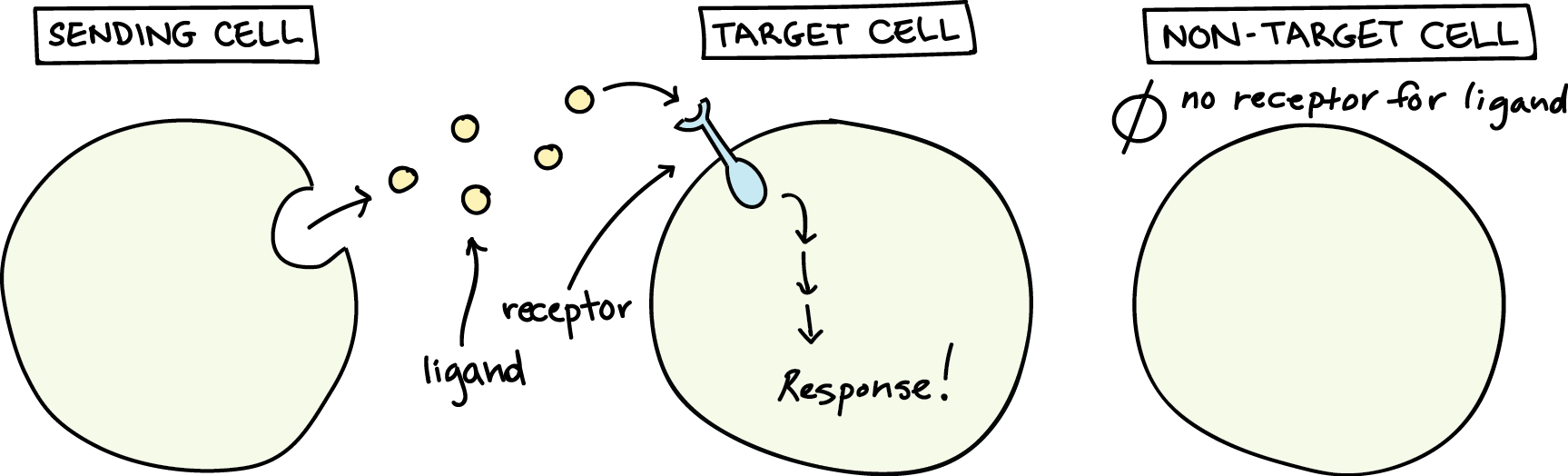
Intro To Chemical Signaling And Communication By Microbes Organismal Biology
Comments
Post a Comment